Ajax介绍
Ajax全称为Asynchronous JavaScript And XML,就是异步的JS和XML。
通过Ajax可以在浏览器中向服务器发送异步请求,最大的优势:无刷新获取数据。
Ajax不是新的编程语言,而是一种将现有的标准组合在一起使用的新方式.
HTTP协议
请求报文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 、、、
行 GET /s?ie=utf-8 HTTP/1.1
头 Host:
Cookie:
Content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
User-Agent: chrome 83
空行
体
、、、
|
响应报文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| 、、、
行 HTTP/1.1 200 ok
头 Centent-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
Content-length: 2048
Content-encoding: gzip
空行
体 <html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html>
、、、
404 找不到资源
403 禁止
401 没有权限
500 内部错误
|
原生AJAX
GET请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
2.初始化 设置请求方法和 url
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server?a=100&b=200&c=300');
3.发送请求
xhr.send();
4.事件绑定 处理服务端返回的结果
xhr.onreadystattechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >= 200 $$ xhr.status <300){
console.log(xhr.status);
console.log(xhr.statusText);
concole.log(xhr.getAllResponseHeaders());
console.log(xhr.response);
}
}
}
|
POST请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
2.初始化 设置请求方法和 url
xhr.open('POST','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server?a=100&b=200&c=300');
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
xhr.setRequestHeader('name','tom');
3.发送请求,设置参数
xhr.send('1231123.1231');
4.事件绑定
xhr.onreadystattechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >= 200 $$ xhr.status <300){
console.log(xhr.response);
}
}
}
|
响应json
方式一:手动转换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server-json');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystattechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >= 200 $$ xhr.status <300){
console.log(xhr.response);
let data = JSON.parse(xhr.response)
}
}
}
|
方式二:设置响应体数据格式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server-json');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystattechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >= 200 $$ xhr.status <300){
console.log(xhr.response);
document.querySelector('div').innerHTML = xhr.response.name;
}
}
}
|
IE缓存问题
在IE浏览器上,发送请求后会对结果根据URL进行缓存,当服务端变更后,因为URL未改变,直接从缓存拿数据,导致最新的结果不能及时呈现
1
2
3
4
| const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/ie?t=+Date.now()');
xhr.send();
...
|
请求超时与网络异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.timeout = 2000;
xhr.ontimeout = function(){
alert('网络异常,请稍后重试');
}
xhr.onerror = function(){
alert('你的网络出现了问题');
}
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/delay');
xhr.send();
...
|
取消请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| let x = null;
x = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/ie?t=+Date.now()');
xhr.send();
...
x.abort();
|
防止重复请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| let x = null;
let isSending = false;
if(isSending) x.abort();
x = new XMLHttpRequest();
isSending = true;
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server-json');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystattechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
isSending = false;
...
}
}
|
jQuery发送AJAX
$.get
1
2
3
| $.get('http://127.0.0.1:8888/jquery-server',{a:100,b:200},function(data){
console.log(data);
},'json')
|
$.post
1
2
3
| $.post('http://127.0.0.1:8888/jquery-server',{a:100,b:200},function(data){
console.log(data);
},'json')
|
$.ajax通用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| $.ajax({
url:'http://127.0.0.1:8888/jquery-server',
data:{a:100,b:200},
type:'GET',
dataType:'json',
timeout:2000,
success: function(data){
console.log(data);
},
error: function(){
concole.log('失败了');
},
headers:{
c:300,
d:400
}
})
|
Axios发送AJAX
axios.get
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
...
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://127.0.0.1:8888'
axios.get('URL',{请求信息)
axios.get('axios-server',{
params:{
id:100,
},
headers:{
name:'tom'
}
}).then(value=>{
concole.log(value);
})
|
axios.post
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
...
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://127.0.0.1:8888'
axios.post('URL',{请求体},{其他参数})
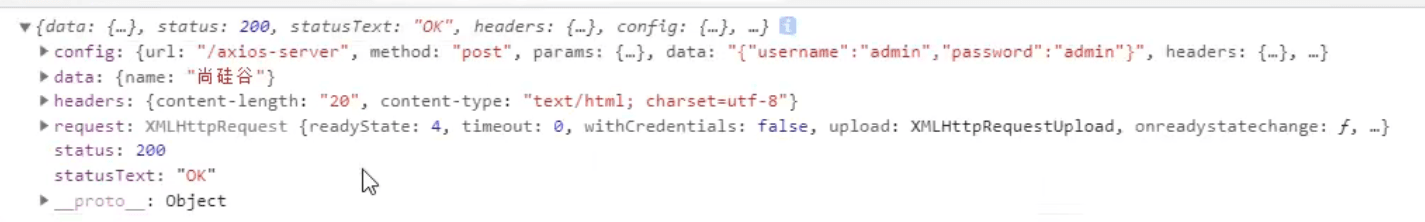
axios.post('axios-server',{
username:'admin',
password:'admin'
},{
params:{
id:100,
},
headers:{
name:'tom'
}
}).then(value=>{
concole.log(value);
})
|
axios通用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| axios({
method:'POST',
url:'axios-server',
params:{
id:1,
},
headers:{
a:100,
},
data:{
username:'admin',
password:'admin',
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response.status);
console.log(response.statusText);
console.log(response.headers);
concole.log(response.data);
})
|
Fetch
Fetch API 提供了一个 JavaScript 接口,用于访问和操纵 HTTP 管道的一些具体部分,例如请求和响应。它还提供了一个全局 fetch() 方法,该方法提供了一种简单,合理的方式来跨网络异步获取资源。是XMLHttpRequest 的理想替代方案。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| fetch('http://127.0.0.1:8888/fetch-server?vip=10',{
method:'POST',
headers:{
name:'tom'
},
body:'username=admin&password=admini',
}).then(response => {
return response.json();
}).then(response => {
concole.log(response);
})
|

